2.1 Molecular Modeling
2.1.3 Homology modeling
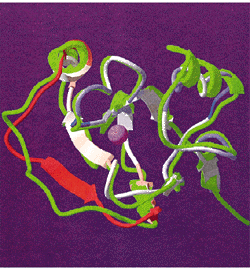 |
| Correlation of the probability of local structural
difference calculated in a window of 11 residues using the
analytical formulae for structural significance of sequence alignment
with the RMS deviation of the backbone Ca
atoms between the template and the experimentally determined
structure for T0009. The reliability function is shown by color (blue,
reliable; red, unreliable) on a structural superposition of our model
of T0009 and the experimental structure (green ribbon). |
Five models by homology containing insertions and deletions and ranging from 33% to 48% sequence
identity to the known homologue, and one high sequence identity (85%) model were built for the CASP2
meeting. For all five low identity targets: (i) our starting models were improved by the Internal Coordinate
Mechanics (ICM) energy optimization, (ii) the refined models were consistently better than those built
with the automatic SWISS-MODEL program, and (iii) the refined models differed by less than 2% from the
best model submitted, as judged by the residue contact area difference (CAD) measure [Abagyan,
R.A., Totrov, M.J. Mol. Biol. 268:678-685, 1997]. The CAD measure is proposed for ranking models built by
homology instead of global root-mean-square deviation, which is frequently dominated by insignificant
yet large contributions from incorrectly predicted fragments or side chains. We demonstrate that the
precise identification of regions of local backbone deviation is an independent and crucial step in the
homology modeling procedure after alignment, since aligned fragments can strongly deviate from the
template at various distances from the alignment gap or even in the ungapped parts of the alignment.
We show that a local alignment score can be used as an indicator of such local deviation. While four
short loops of the meeting targets were predicted by database search, the best loop 1 target T0028, for
which the correct database fragment was not found, was predicted by Internal Coordinate Mechanics
global energy optimization at 1.2 A accuracy. A classification scheme for errors in homology modeling is
proposed.
[Proteins - 1997] [PDF]
