2.4 Methods and Algorithms
2.4.6 Protein 3D model accuracy evaluation
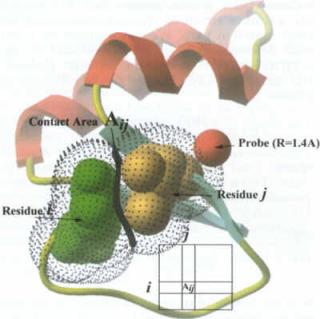 |
| The surface area of contact between the two residues i and j. Absolute differences between the Aij values for two
different models are accumulated in the CAD number. |
A simple unified measure to evaluate the accuracy of three-dimensional atomic protein models is
proposed. This measure is a normalized sum of absolute differences of residue-residue contact surface
areas calculated for a reference structure and a model. It employs more rigorous quantitative
evaluation of a contact than previously proposed contact count based measures. We argue that the
contact area difference (CAD) number is a robust single measure to evaluate protein structure
predictions in a wide range of model accuracies, from ab initio and threading models to models by
homology, since it reflects both local secondary structure and packing geometry, is smooth, continuous
and threshold-free, is not sensitive to typical crystallographic errors and ambiguities, adequately
penalizes domain and/or secondary structure rearrangements and protein plasticity, and has
consistent linear and matrix representations for more detailed analysis. The CAD quality of
crystallographic structures, NMR structures, models by homology, and unfolded and misfolded
structures is evaluated. It is shown that the CAD number discriminates between models better than
Cartesian root-mean-square deviation (cRMSD). The source code of the program calculating the CAD
measures is available from the authors.
[J. Molecular Biology - 1997] [PDF]
