| 2 Research | |
| Section Intro | Threading and energy profiles | structural similarities | functional annotation | sequence |
Sequence comparison remains a powerful tool to assess the structural relatedness of two proteins. To improve the reliability of recognition in the twilight zone of sequence identities between 15 and 35%, we performed an exhaustive alignment of sequences of protein domains with known 3D folds and derived a set of functions which represent structural significance and positional accuracy of any sequence alignment. The subset of 1,347,037 alignments between sequences of structurally unrelated domains was used to derived accurate probability functions of a structurally insignificant alignment at a given sequence identity, sequence similarity and alignment score. It is shown that sequence identity and sequence similarity measures are poor indicators of structural relatedness in the twilight zone, while the alignment score allows much better discrimination between alignments of structurally related sequences and unrelated ones, with the expected recognition error being three times lower. The derived functions can be used for fold recognition.
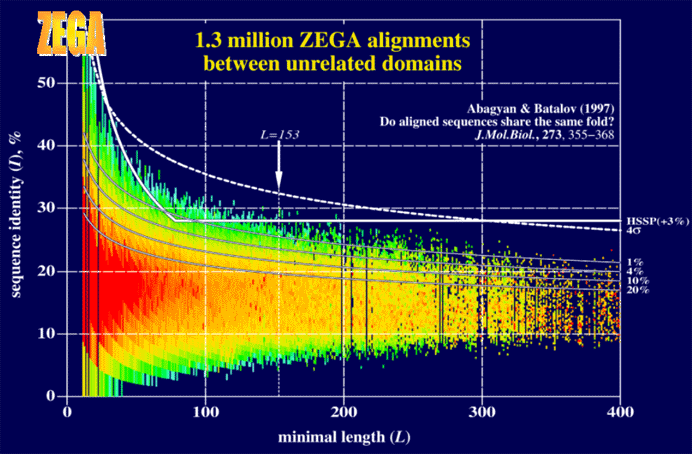 |
| Distribution of sequence identities in 1,330,931 pairwise Needleman & Wunsch (1970) alignments with zero end gap penalties between sequences of structurally unrelated protein domains as a function of length of the shorter sequence (L). Only alignments with sequence overlap greater than 50% were retained. Coloring represents the probability density (i.e. the fraction of alignments with the given number of identical residues and minimal sequence length), with higher density represented by red color. Dark blue corresponds to zero density (no alignments). At low sequence identities, two sequences cannot be aligned with the global alignment algorithm utilizing a non-positive comparison matrix. This explains the zero density at very low identities. The upper continuous curve combined with the straight line shows the Sander & Schneider (1991) dependence of sequence identity threshold with the safety margin m = 3%, as used in the HSSP database. The broken line is the 4sigma-level threshold for this comparison setup. The four continuous curves represent the derived thresholds at the following levels: 1, 4, 10 and 20%, from top to bottom. |